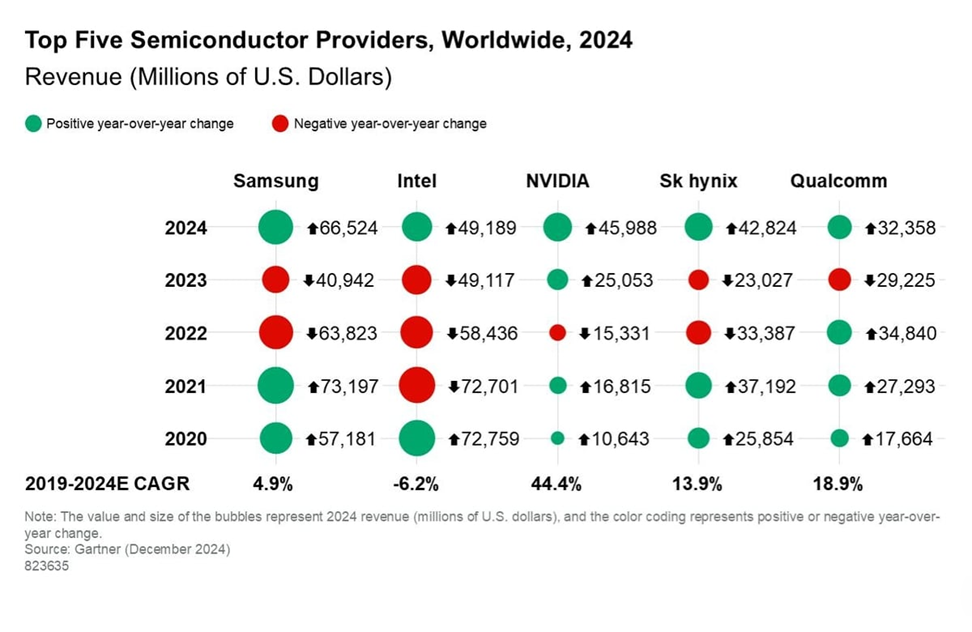
According to the latest statistics from Gartner, Samsung Electronics is expected to regain its position as the largest semiconductor supplier in terms of revenue, surpassing Intel. However, this data does not include TSMC, the world's largest foundry.
Samsung Electronics' revenue appears to have rebounded despite poor performance due to deteriorating profitability of DRAM and NAND flash memory. SK Hynix, which has a strong advantage in the high-bandwidth memory (HBM) market, is expected to rise to fourth place in the world this year.
Market research firm Gartner predicts that global semiconductor revenue will increase by 18.1% from the previous year (US$530 billion) to US$626 billion in 2024. Among them, the total revenue of the top 25 semiconductor suppliers is expected to increase by 21.1% year-on-year, and the market share is expected to increase from 75.3% in 2023 to 77.2% in 2024, an increase of 1.9 percentage points.
Against the backdrop of a global economic downturn, the polarization of demand for AI semiconductor products such as HBM and traditional products has intensified, resulting in mixed performance for semiconductor companies. Samsung Electronics is expected to regain the top spot lost to Intel in 2023 within a year. Samsung's semiconductor revenue last year was expected to be US$66.5 billion, up 62.5% from the previous year.
Gartner noted that "after two consecutive years of decline, memory product revenue rebounded significantly last year," and predicted that Samsung's average annual growth rate over the past five years will reach 4.9%.
Gartner predicts that global semiconductor revenue will grow 17% in 2024. According to Gartner's latest forecast, global semiconductor revenue is expected to grow 16.8% to $624 billion in 2024. The market is expected to decline 10.9% in 2023 to $534 billion.
"As 2023 draws to a close, strong demand for chips such as graphics processing units (GPUs) that support AI workloads will not be enough to offset the double-digit decline in the semiconductor industry this year," said Alan Priestley, vice president and analyst at Gartner. "Declining demand from smartphone and PC customers, coupled with weak spending in data centers and hyperscale data centers, is affecting revenue declines this year."
However, 2024 is expected to be a rebound year, with revenues for all chip types growing, driven by double-digit growth in the memory market.
The global memory market is expected to decline by 38.8% in 2023, but rebound in 2024 with a 66.3% increase. NAND flash memory revenue is expected to fall by 38.8% in 2023 to $35.4 billion, due to weak demand and oversupply leading to falling prices. In the next 3-6 months, NAND prices are expected to bottom out and the situation for suppliers will improve. Gartner analysts predict a strong recovery in 2024, with revenue rising to $53 billion, a year-on-year increase of 49.6%.
Due to severe oversupply and insufficient demand, DRAM suppliers are chasing market prices to reduce inventory. The DRAM market oversupply is expected to continue through the fourth quarter of 2023, leading to a price rebound. However, the full impact of the price increase will not be felt until 2024, when DRAM revenue is expected to grow 88% to $87.4 billion.
The development of generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) and large language models is driving demand for high-performance GPU servers and accelerator cards in data centers. This requires the deployment of workload accelerators in data center servers to support the training and inference of AI workloads. Gartner analysts estimate that by 2027, the integration of AI technology into data center applications will result in more than 20% of new servers containing workload accelerators.
Post time: Jan-20-2025

